转自:https://blog.csdn.net/dataiyangu/article/details/86440836#1__3
1. 无锁类的原理详解
简介:1.1. CAS1.2. CPU指令2. 无锁类的使用2.1. AtomicInteger2.1.1. 概述2.1.2. 主要接口2.1.3. 主要接口的实现例子2.2. Unsafe2.2.1. 概述2.2.2. 主要接口2.3. AtomicReference2.3.1. 概述2.3.2. 主要接口2.4. AtomicStampedReference2.4.1. 概述2.5. AtomicIntegerArray2.5.1. 概述2.5.2. 主要接口例子源码解析2.6. AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater2.6.1. 概述2.6.2. 主要接口 AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater()例子2.6.3. 小说明3. 无锁算法详解3.1. 无锁的Vector实现1. 无锁类的原理详解
简介:前面已经介绍过无锁:– 无障碍无障碍是一种最弱的非阻塞调度自由出入临界区无竞争时,有限步内完成操作有竞争时,回滚数据有竞争时,回滚数据好进不好出,很容易进去,但是进去发现很多线程竞争相同的资源的时候,会需要回滚数据,比如要读取xy,已经读过了x,读到y的时候发现在竞争,会从x重新读。– 无锁
是无障碍的保证有一个线程可以胜出while (!atomicVar.compareAndSet(localVar, localVar+1)) { localVar = atomicVar.get();}因为无障碍中,如果存在不断的竞争,将会所有的都出不来,所以无锁就需要每次竞争都能胜出一个,这样保证程序能够顺畅的执行下去。1.1. CAS
CAS算法的过程是这样:它包含3个参数CAS(V,E,N)。V表示要更新的变量,E表示预期值,N表示新值。仅当V 值等于E值时,才会将V的值设为N,如果V值和E值不同,则说明已经有其他线程做了更新,则当前线程什么 都不做。最后,CAS返回当前V的真实值。CAS操作是抱着乐观的态度进行的,它总是认为自己可以成功完成 操作。当多个线程同时使用CAS操作一个变量时,只有一个会胜出,并成功更新,其余均会失败。失败的线程 不会被挂起,仅是被告知失败,并且允许再次尝试,当然也允许失败的线程放弃操作。基于这样的原理,CAS 操作即时没有锁,也可以发现其他线程对当前线程的干扰,并进行恰当的处理。CAS是一个原子操作,是由一条cpu指令完成的。
java中提供了很多无所类的使用,如果一个线程被挂起,将会消耗八万个时光周期,但是如果是无锁的,最多只是循环,也就只会消耗几个时光周期,所以无锁的方式比阻塞的方式要好很多。
1.2. CPU指令
cmpxchg/*accumulator = AL, AX, or EAX, depending on whethera byte, word, or doubleword comparison is being performed */if(accumulator == Destination) { ZF = 1; //判断是否和期望值相等,相等的话就给一个转换标志。同时进行转换。Destination = Source; }else { ZF = 0; //不相等的话就给一个不转换的标志。同时不转换。accumulator = Destination; }12345678910这是一个原子操作是安全的。2. 无锁类的使用
2.1. AtomicInteger2.1.1. 概述Number2.1.2. 主要接口
public final int get()//取得当前值public final void set(int newValue)//设置当前值public final int getAndSet(int newValue)//设置新值,并返回旧值public final boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int u)//如果当前值为expect,则设置为upublic final int getAndIncrement() //当前值加1,返回旧值public final int getAndDecrement()//当前值减1,返回旧值public final int getAndAdd(int delta)//当前值增加delta,返回旧值public final int incrementAndGet() //当前值加1,返回新值public final int decrementAndGet() //当前值减1,返回新值public final int addAndGet(int delta)//当前值增加delta,返回新值2.1.3. 主要接口的实现
compareAndSet方法//expect期望值,update更新的新值,成功返回true,失败返回false
public final boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update) { return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, valueOffset, expect, update); } //unsafe是不安全的,java将指针进行了屏蔽封装,而unsafe会提供类似指针的操作,对这个类的偏移量上的期望值12345偏移量valueOffset哪里来的?valueOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
1getAndIncrement方法//返回当前值,并且加一
public final int getAndIncrement() { for(;;){ int current = get(); int next = current + 1; if(compareAndSet(current,next)) return current; } }1
2345678910get是得到当前这个类的private volatile int value;这个值加一,然后compareAndSet,如果当前的值和期望值相等的时候返回当前的这个值,否则,继续循环,和无锁的机制是一样的。如果在判断之前有其他的线程拿到了current值,在下面的if将会失败例子
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;public class Test {
static AtomicInteger i = new AtomicInteger(); public static class AddThread implements Runnable{ public void run(){ for (int j = 0; j < 10000; j++) { i.incrementAndGet(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread[] ts = new Thread[10]; for (int k = 0; k < 10; k++) { ts[k] = new Thread(new AddThread()); } for (int k = 0; k < 10; k++) { ts[k].start(); } for (int k = 0; k < 10; k++) { ts[k].join(); } System.out.println(i); }}
2.2. Unsafe
2.2.1. 概述非安全的操作,比如: 根据偏移量设置值 、park() 、底层的CAS操作非公开API,在不同版本的JDK中, 可能有较大差异static {
try { valueOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset (AtomicInteger.class.getDeclaredField("value")); } catch (Exception ex) { throw new Error(ex); } }1
234567拿到value这个字段在本类(相当于c中的首地址)中的偏移量是多少。2.2.2. 主要接口
//获得给定对象偏移量上的int值public native int getInt(Object o, long offset); //设置给定对象偏移量上的int值public native void putInt(Object o, long offset, int x); //获得字段在对象中的偏移量public native long objectFieldOffset(Field f); //设置给定对象的int值,使用volatile语义public native void putIntVolatile(Object o, long offset, int x); //获得给定对象对象的int值,使用volatile语义public native int getIntVolatile(Object o, long offset); //和putIntVolatile()一样,但是它要求被操作字段就是volatile类型的 public native void putOrderedInt(Object o, long offset, int x);2.3. AtomicReference
2.3.1. 概述对象的引用对引用进行修改 是一个模板类,抽象化了数据类型2.3.2. 主要接口
get()set(V) compareAndSet() getAndSet(V)大部分的方法和compareAndSet差不多。例子: import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;public class Test {
public final static AtomicReference<String> atomicStr = new AtomicReference<String>("abc"); public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { final int num = i; new Thread() { public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(Math.abs((int)Math.random()*100)); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if (atomicStr.compareAndSet(("abc"), "def")) { System.out.println("Thread"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+"change value to"+atomicStr.compareAndSet(("abc"), "def")); }else{ System.out.println("Thread"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+"FALED"); } } }.start(); } }}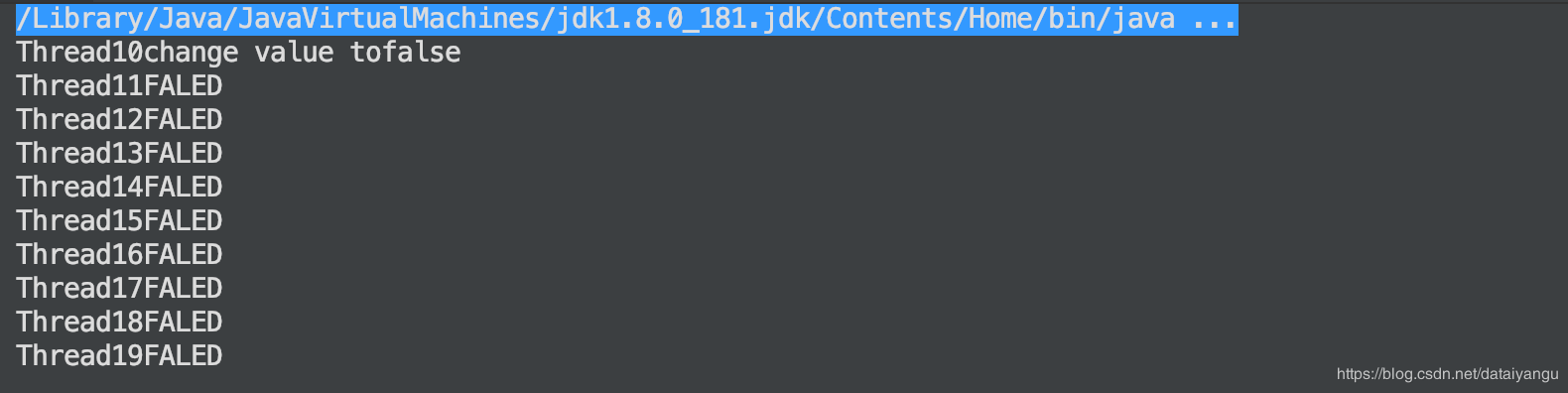
2.4. AtomicStampedReference
和对象的引用差不多
stamped表示时间戳、唯一性等2.4.1. 概述
ABA问题
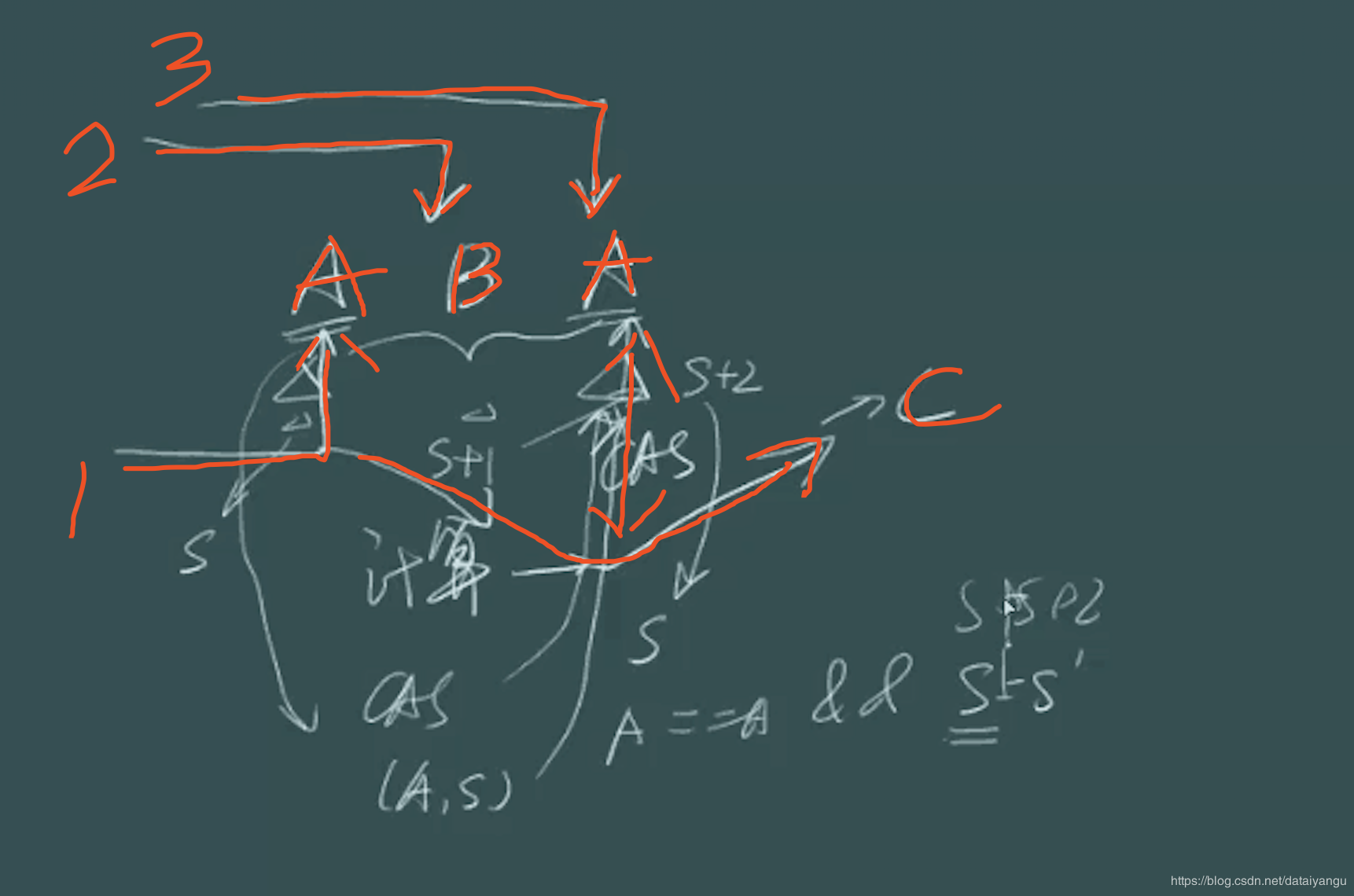
如图,一个值为A,期初一个线程1拿到它,然后做相关的操作,这个时候线程2拿到这个A并且改为了B,线程3拿到了B改为了A,这个时候线程1将拿到的A和讲过了线程2 线程3后的A进行比较,相同的话A就改为C。
发现是没问题的,因为A还是变为了A,如果是加法,没问题,可是如果比较关注中间的过程呢?比如网吧充钱,没钱机器就自动冲,可是只能自动充值一次,这个时候第二次还是到了临界点呢??这个时候就需要给一个时间戳或者唯一的标识。每次改变的时候都传递一个包含A和时间戳的对象,每次在比价A的同时比较时间戳。源码解析://将原来的value做了一层封装分为了reference和stamp
private static class Pair<T> { final T reference; final int stamp; private Pair(T reference, int stamp) { this.reference = reference; this.stamp = stamp; } static <T> Pair<T> of(T reference, int stamp) { return new Pair<T>(reference, stamp); } }//compareAndSet的参数也由原来的两个,变为了四个,包括期望值和新的值
public boolean compareAndSet(V expectedReference, V newReference, int expectedStamp, int newStamp) { Pair<V> current = pair; return //当两个都相等的时候才有机会向下执行 expectedReference == current.reference && expectedStamp == current.stamp && ((newReference == current.reference && newStamp == current.stamp) || casPair(current, Pair.of(newReference, newStamp))); }//jdk中经常会有函数叫做cas...来更新列表的头部、尾部等操作
//pairOffset就是private boolean casPair(Pair<V> cmp, Pair<V> val) { return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, pairOffset, cmp, val); } 2.5. AtomicIntegerArray2.5.1. 概述支持无锁的数组2.5.2. 主要接口
//获得数组第i个下标的元素public final int get(int i)//获得数组的长度public final int length()//将数组第i个下标设置为newValue,并返回旧的值public final int getAndSet(int i, int newValue) //进行CAS操作,如果第i个下标的元素等于expect,则设置为update,设置成功返回true public final boolean compareAndSet(int i, int expect, int update)//将第i个下标的元素加1public final int getAndIncrement(int i) //将第i个下标的元素减1public final int getAndDecrement(int i) //将第i个下标的元素增加delta(delta可以是负数) public final int getAndAdd(int i, int delta)例子
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerArray;import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;public class Test {
static AtomicIntegerArray arr = new AtomicIntegerArray(10);public static class AddThread implements Runnable {
public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { arr.getAndIncrement(i % arr.length());}
} } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread[] ts = new Thread[10]; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { ts[i] = new Thread((new AddThread())); } for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { ts[i].start();}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { ts[i].join();}
System.out.println(arr); }} 如果是不安全的话,不会每个都是1000,应该比这个小。源码解析
private static final int base = unsafe.arrayBaseOffset(int[].class);public final int get(int i) {
return getRaw(checkedByteOffset(i)); }private int getRaw(long offset) {
//数组所在的基地址开始取offset的偏移量 return unsafe.getIntVolatile(array, offset);}//返回第i个元素在数组中的偏移量是多少private long checkedByteOffset(int i) { if (i < 0 || i >= array.length) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("index " + i);return byteOffset(i);
}private static long byteOffset(int i) { //i偏移了shift的数值 return ((long) i << shift) + base; //通过下面的计算 i左移两位(二进制,即在末尾加两个零 //,如果是十进制就是乘以4) }static { //数组中每个元素有多宽,int就是4(每个int是4个byte) int scale = unsafe.arrayIndexScale(int[].class); if ((scale & (scale - 1)) != 0) throw new Error("data type scale not a power of two"); //shift的值 //numberOfLeadingZeros前导零,一个数字化成二进制 //前面的零的个数 //4------> 00000....100 32-3=29 //4的前导零就是29 shift = 31 - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(scale); //所以shift=2 } 2.6. AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater2.6.1. 概述让普通变量也享受原子操作希望拥有原子操作,但是不改变原原子的类型。使用尽量少的代码、在不改变原来类型的基础上、做出较少的改变来实现原子操作。2.6.2. 主要接口 AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater()
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdate.newUpdate()incrementAndGet()例子
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerArray;import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater;import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;public class Test {
public static class Candidate{ int id; volatile int score; }public final static AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<Candidate> scoreUpdater =
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(Candidate.class, "score"); public static AtomicInteger allScore = new AtomicInteger();public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
final Candidate stu = new Candidate(); Thread[] threads = new Thread[10000]; for (int i = 0; i <10000 ; i++) { threads[i] = new Thread(){ public void run(){ if (Math.random()>0.4){ scoreUpdater.incrementAndGet(stu); allScore.incrementAndGet(); } } }; threads[i].start(); } for (int i = 0; i <10000 ; i++) { threads[i].join(); } System.out.println("sore="+stu.score); System.out.println("allScore="+allScore); }} 通过AtomicInteger来验证,发现是相同的安全的结果,主要就是上面提到的两个方法,通过反射实现的。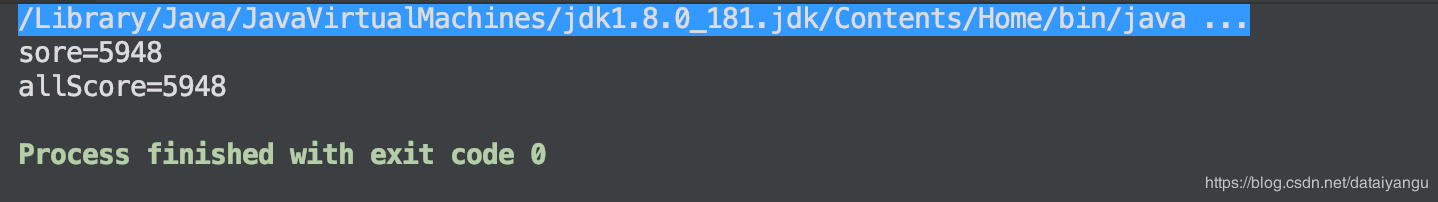
2.6.3. 小说明
Updater只能修改它可见范围内的变量。因为Updater使用反射得到这个变量。如果变量不可见,就会出错。比如如果score申明为private,就是不可行的。为了确保变量被正确的读取,它必须是volatile类型的。如果我们原有代码中未申明这个类型,那么简单得 申明一下就行,这不会引起什么问题。由于CAS操作会通过对象实例中的偏移量直接进行赋值,因此,它不支持static字段(Unsafe. objectFieldOffset()不支持静态变量)。3. 无锁算法详解jdk中的vector是有锁的。源码解析:/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this Vector. * * @param e element to be appended to this Vector * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) * @since 1.2 */ public synchronized boolean add(E e) { //记录vector被修改的次数 modCount++; // vector底层是数组 // 判断时候越界,如果越界了就进行扩展,扩展代码在下面 ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1); //不越界就将e加在后面 elementData[elementCount++] = e; return true; } // 是一个同步的方法,每次只有一个线程能进行add操作,所有的元素都保存在elementData 中 private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); }private void grow(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code int oldCapacity = elementData.length; //扩展增量(扩容)capacityIncrement可以自己制定,如果自己不指定的话就 //是默认的oldCapacity+oldCapacity------>newCapacity也就是 //乘以二 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ? capacityIncrement : oldCapacity); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); //把老元素放到新的元素中去 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } //创建了一个新的数组,把原来的数组复制过去。 public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class) ? (T[]) new Object[newLength] : (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength); System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0, Math.min(original.length, newLength)); return copy; }12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940414243444546474849注意看里面的注释很重要:提取出来几个vector底层是数组判断时候越界,如果越界了就进行扩展,add是一个同步的方法(有锁的),每次只有一个线程能进行add操作扩展增量(扩容)capacityIncrement可以自己制定,如果自己不指定的话就是默认的oldCapacity+oldCapacity------>newCapacity也就是乘以二(有次面试我被问过)!!!所以当扩容的数字很大的时候,建议给个扩容的大小把老元素放到新的元素中去创建了一个新的数组,把原来的数组复制过去。3.1. 无锁的Vector实现
这里只将源码贴出来和普通的vector实现的区别是原来的vector是一维数组,而这里的数组是二维的数组,为什么用二维数组?二维数组中的第一个容量是n,第二个就是2n,第三个就是4n。。。。以此类推,就像是一个个不同容量的篮子。FIRST_BUCKET_SIZE给定第一个篮子的大小N_BUCKET有多少个篮子private final AtomicReferenceArray<AtomicReferenceArray> buckets;通过AtomicReferenceArray的二重数组来封装这些篮子。AtomicReferenceArray和AtomicArray差不多只是将array的值换成了对象。有个分析的很不错的博文:
http://reimuwang.org/2018/05/17/Java 并发-无锁的Vector实现//*
* Copyright (c) 2007 IBM Corporation * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */package main.java.org.amino.ds.lockfree;import java.util.AbstractList;import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReferenceArray;/** * It is a thread safe and lock-free vector. * This class implement algorithm from:<br> * * Lock-free Dynamically Resizable Arrays <br> * * Damian Dechev, Peter Pirkelbauer, and Bjarne Stroustrup<br> * Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-3112<br> * {dechev, peter.pirkelbauer}@tamu.edu, bs@cs.tamu.edu * * * @author Zhi Gan * * @param <E> type of element in the vector * */public class LockFreeVector<E> extends AbstractList<E> { private static final boolean debug = false; /** * Size of the first bucket. sizeof(bucket[i+1])=2*sizeof(bucket[i]) */ private static final int FIRST_BUCKET_SIZE = 8; /** * number of buckets. 30 will allow 8*(2^30-1) elements */ private static final int N_BUCKET = 30; /** * We will have at most N_BUCKET number of buckets. And we have * sizeof(buckets.get(i))=FIRST_BUCKET_SIZE**(i+1) */ private final AtomicReferenceArray<AtomicReferenceArray<E>> buckets; /** * @author ganzhi * * @param <E> */ static class WriteDescriptor<E> { public E oldV; public E newV; public AtomicReferenceArray<E> addr; public int addr_ind; /** * Creating a new descriptor. * * @param addr Operation address * @param addr_ind Index of address * @param oldV old operand * @param newV new operand */ public WriteDescriptor(AtomicReferenceArray<E> addr, int addr_ind, E oldV, E newV) { this.addr = addr; this.addr_ind = addr_ind; this.oldV = oldV; this.newV = newV; } /** * set newV. */ public void doIt() { addr.compareAndSet(addr_ind, oldV, newV); } } /** * @author ganzhi * * @param <E> */ static class Descriptor<E> { public int size; volatile WriteDescriptor<E> writeop; /** * Create a new descriptor. * * @param size Size of the vector * @param writeop Executor write operation */ public Descriptor(int size, WriteDescriptor<E> writeop) { this.size = size; this.writeop = writeop; } /** * */ public void completeWrite() { WriteDescriptor<E> tmpOp = writeop; if (tmpOp != null) { tmpOp.doIt(); writeop = null; // this is safe since all write to writeop use // null as r_value. } } } private AtomicReference<Descriptor<E>> descriptor; private static final int zeroNumFirst = Integer .numberOfLeadingZeros(FIRST_BUCKET_SIZE);; /** * Constructor. */ public LockFreeVector() { buckets = new AtomicReferenceArray<AtomicReferenceArray<E>>(N_BUCKET); buckets.set(0, new AtomicReferenceArray<E>(FIRST_BUCKET_SIZE)); descriptor = new AtomicReference<Descriptor<E>>(new Descriptor<E>(0, null)); } /** * add e at the end of vector. * * @param e * element added */ public void push_back(E e) { Descriptor<E> desc; Descriptor<E> newd; do { desc = descriptor.get(); desc.completeWrite(); //desc.size Vector 本身的大小 //FIRST_BUCKET_SIZE 第一个一位数组的大小 int pos = desc.size + FIRST_BUCKET_SIZE; int zeroNumPos = Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(pos); // 取出pos 的前导领 //zeroNumFirst 为FIRST_BUCKET_SIZE 的前导领 int bucketInd = zeroNumFirst - zeroNumPos; //哪个一位数组 //判断这个一维数组是否已经启用 if (buckets.get(bucketInd) == null) { //newLen 一维数组的长度 int newLen = 2 * buckets.get(bucketInd - 1).length(); if (debug) System.out.println("New Length is:" + newLen); buckets.compareAndSet(bucketInd, null, new AtomicReferenceArray<E>(newLen)); } int idx = (0x80000000>>>zeroNumPos) ^ pos; //在这个一位数组中,我在哪个位置 newd = new Descriptor<E>(desc.size + 1, new WriteDescriptor<E>( buckets.get(bucketInd), idx, null, e)); } while (!descriptor.compareAndSet(desc, newd)); descriptor.get().completeWrite(); } /** * Remove the last element in the vector. * * @return element removed */ public E pop_back() { Descriptor<E> desc; Descriptor<E> newd; E elem; do { desc = descriptor.get(); desc.completeWrite(); int pos = desc.size + FIRST_BUCKET_SIZE - 1; int bucketInd = Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(FIRST_BUCKET_SIZE) - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(pos); int idx = Integer.highestOneBit(pos) ^ pos; elem = buckets.get(bucketInd).get(idx); newd = new Descriptor<E>(desc.size - 1, null); } while (!descriptor.compareAndSet(desc, newd)); return elem; } /** * Get element with the index. * * @param index * index * @return element with the index */ @Override public E get(int index) { int pos = index + FIRST_BUCKET_SIZE; int zeroNumPos = Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(pos); int bucketInd = zeroNumFirst - zeroNumPos; int idx = (0x80000000>>>zeroNumPos) ^ pos; return buckets.get(bucketInd).get(idx); } /** * Set the element with index to e. * * @param index * index of element to be reset * @param e * element to set */ /** * {@inheritDoc} */ public E set(int index, E e) { int pos = index + FIRST_BUCKET_SIZE; int bucketInd = Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(FIRST_BUCKET_SIZE) - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(pos); int idx = Integer.highestOneBit(pos) ^ pos; AtomicReferenceArray<E> bucket = buckets.get(bucketInd); while (true) { E oldV = bucket.get(idx); if (bucket.compareAndSet(idx, oldV, e)) return oldV; } } /** * reserve more space. * * @param newSize * new size be reserved */ public void reserve(int newSize) { int size = descriptor.get().size; int pos = size + FIRST_BUCKET_SIZE - 1; int i = Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(FIRST_BUCKET_SIZE) - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(pos); if (i < 1) i = 1; int initialSize = buckets.get(i - 1).length(); while (i < Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(FIRST_BUCKET_SIZE) - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(newSize + FIRST_BUCKET_SIZE - 1)) { i++; initialSize *= FIRST_BUCKET_SIZE; buckets.compareAndSet(i, null, new AtomicReferenceArray<E>( initialSize)); } } /** * size of vector. * * @return size of vector */ public int size() { return descriptor.get().size; } /** * {@inheritDoc} */ @Override public boolean add(E object) { push_back(object); return true; }}